U.S.new ranking
2025-07-06
السمعة العالمية للبحث العلمي: (12.5%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر مجموع نتائج آخر خمس سنوات من استطلاع السمعة الأكاديمية لأفضل الجامعات عالميًا في مجال البحث العلمي.
السمعة الإقليمية للبحث العلمي: (12.5%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر مجموع نتائج آخر خمس سنوات من استطلاع السمعة الأكاديمية لأفضل الجامعات في مجال البحث العلمي في المنطقة الإقليمية. تم تحديد المناطق بناءً على تعريف الأمم المتحدة.
لقد زاد هذا المؤشر الإقليمي بشكل كبير من التنوع الدولي للتصنيفات، حيث ركز على قياس آراء الأكاديميين حول الجامعات الأخرى ضمن منطقتهم. تُعد تصنيفات U.S. News هي التصنيفات العالمية الوحيدة التي تستخدم هذا المؤشر، وتشير نسخة 2021 إلى السنة السابعة من إدراجه.
الإصدارات/ الأبحاث المنشورة (10%)
يقيس هذا المؤشر إنتاجية البحث الإجمالية للجامعة، استنادًا إلى العدد الكلي للأبحاث العلمية، المراجعات، المقالات، والملاحظات، التي تحتوي على مشاركين من الجامعة وتُنشر في مجلات عالية الجودة وذات تأثير. يرتبط هذا المؤشر ارتباطًا وثيقًا بحجم الجامعة. كما يتأثر أيضًا بتخصصات الجامعة، حيث إن بعض التخصصات، مثل الطب، تنشر أكثر من غيرها.
الكتب: (2.5%)
الكتب تعد وسيلة مهمة للنشر في البحث العلمي، خاصة في مجالات العلوم الاجتماعية والفنون والعلوم الإنسانية. يوفر مؤشر التصنيف هذا إضافة مفيدة للبيانات المتعلقة بالمقالات العلمية، ويُعطي تمثيلًا أفضل للجامعات التي تركز على العلوم الاجتماعية والفنون والعلوم الإنسانية.
المؤتمرات (2.5%)
تعد المؤتمرات الأكاديمية من الأماكن الهامة للتواصل العلمي، خصوصًا في التخصصات المرتبطة بالهندسة وعلوم الكمبيوتر. إن النشر الرسمي لأعمال المؤتمرات يمكن أن يمثل تقدمًا حقيقيًا في الأبحاث في بعض المجالات التي قد لا تكون قد تم توثيقها أو نشرها في أماكن أخرى.Top of FormBottom of Form
تأثير الاستشهادات: (10%)
يمثل العدد الإجمالي للاستشهادات لكل بحث التأثير العام لأبحاث الجامعة، وهو مستقل عن حجم الجامعة أو عمرها. يتم تطبيع القيمة لتجاوز الاختلافات في مجال البحث، سنة نشر البحث، ونوع النشر، مما يضمن مقارنة عادلة بين الجامعات التي تعمل في مجالات أكاديمية مختلفة أو في فترات زمنية متنوعة.Top of FormBottom of Form
إجمالي الاستشهادات: (7.5%)
يقيس هذا المؤشر مدى تأثير الجامعة في المجتمع البحثي العالمي. يتم تحديده من خلال ضرب عامل ترتيب المنشورات بعامل تأثير الاستشهادات المعدل. تم تطبيع إجمالي الاستشهادات لتجاوز الاختلافات في مجال البحث، سنة نشر البحث، ونوع النشر، مما يضمن مقارنة عادلة بين الجامعات التي تعمل في مجالات أكاديمية مختلفة أو في فترات زمنية متنوعة.
عدد المنشورات التي تندرج ضمن أعلى 10% من المنشورات الأكثر استشهادًا: (12.5%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر عدد الأبحاث التي تم تصنيفها ضمن أعلى 10% من الأبحاث الأكثر استشهادًا في العالم في مجالاتها الخاصة. يتم إعطاء كل بحث درجة مئوية تمثل مكانتها من حيث ترتيب الاستشهادات مقارنة بالأبحاث المماثلة التي تتمتع بنفس سنة النشر، التخصص، ونوع الدراسة.
نسبة المنشورات الإجمالية التي تقع ضمن أعلى 10% من المنشورات الأكثر استشهادًا: (10%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر نسبة الأبحاث التي تنتجها الجامعة والتي تقع ضمن أعلى 10% من الأوراق الأكثر استشهادًا في العالم، وذلك حسب المجال وسنة النشر. يُعد هذا المعيار مقياسًا لمقدار البحث الممتاز الذي تنتجه الجامعة، وهو مستقل عن حجم الجامعة.
التعاون الدولي – بالنسبة للدولة (5%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر نسبة الأبحاث التي تحتوي على مؤلفين دوليين في الجامعة مقارنة بنسبة الأبحاث التي يشارك فيها مؤلفون دوليون في الدولة التي توجد فيها الجامعة. يُظهر هذا المؤشر مدى انتشار الأبحاث عالميًا في الجامعة مقارنةً بالمعدل العام للأبحاث الدولية في البلد الذي تنتمي إليه المؤسسة.
التعاون الدولي: (5%)
يعكس هذا المؤشر نسبة الأبحاث التي تحتوي على مؤلفين دوليين من إجمالي الأبحاث التي تنشرها المؤسسة. يُعتبر هذا المعيار مقياسًا آخر للجودة.Top of FormBottom of Form

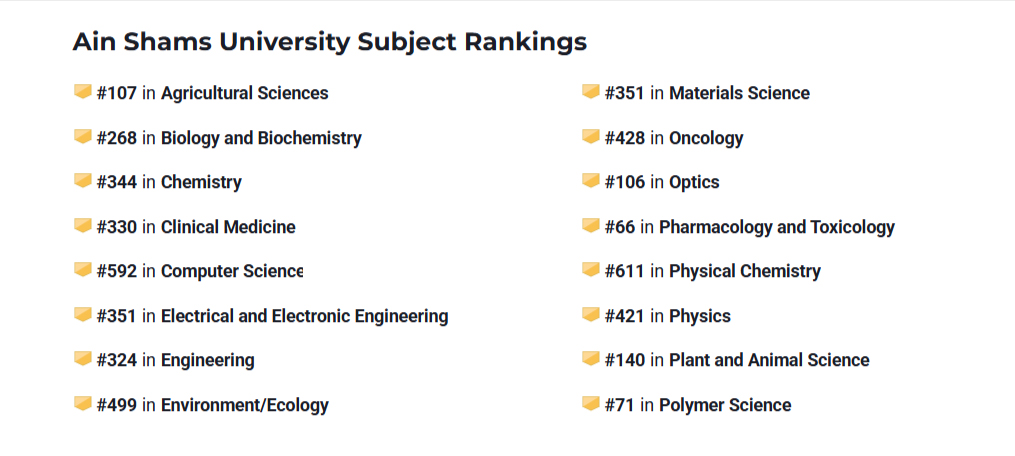
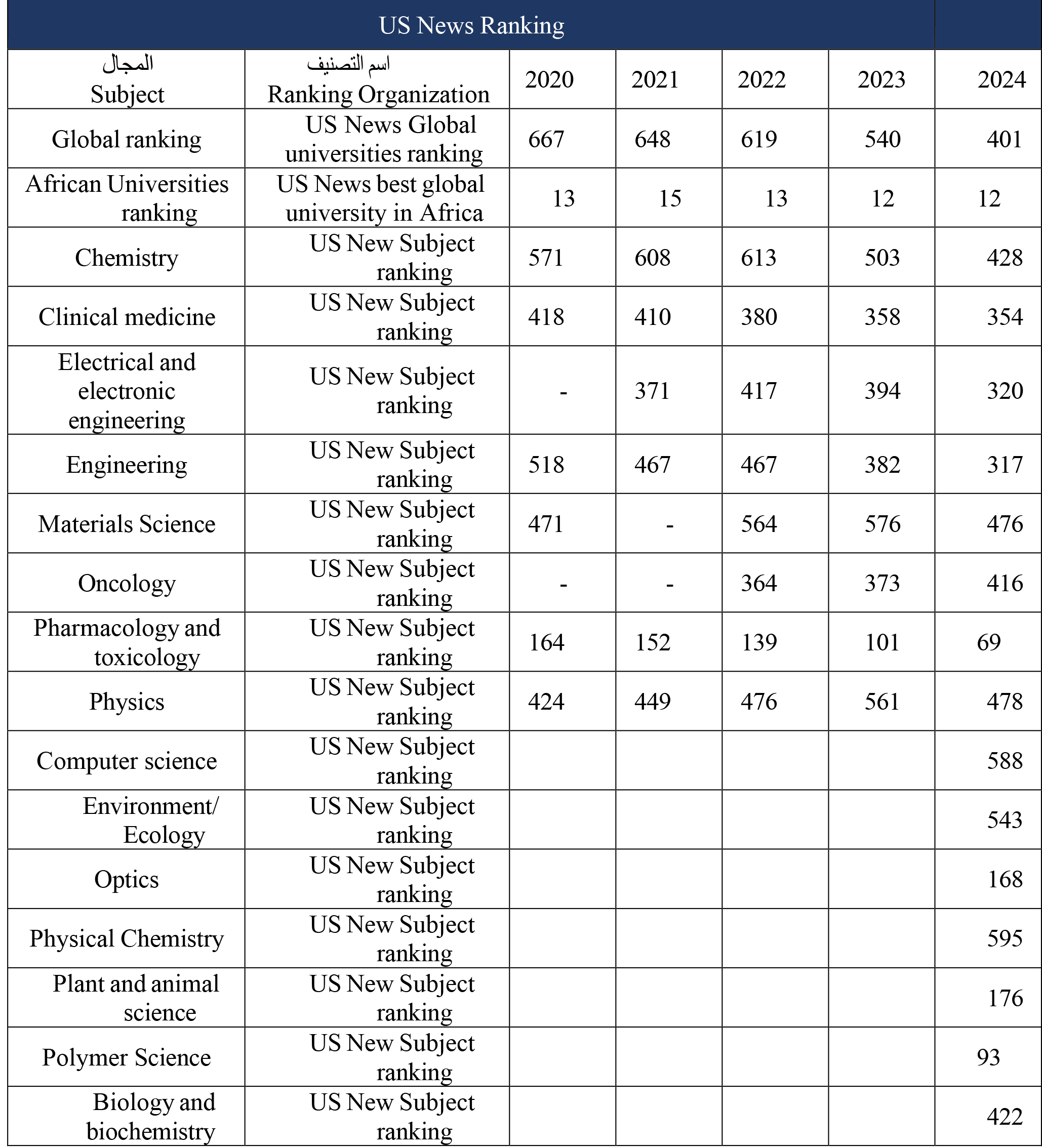
تصنيف الاعوام السابقة
To request feedback or learn more about our rankings


.svg)

